Differences between UTI and Yeast Infection
Contents
Urinary Tract Infection vs. Yeast Infection[edit]
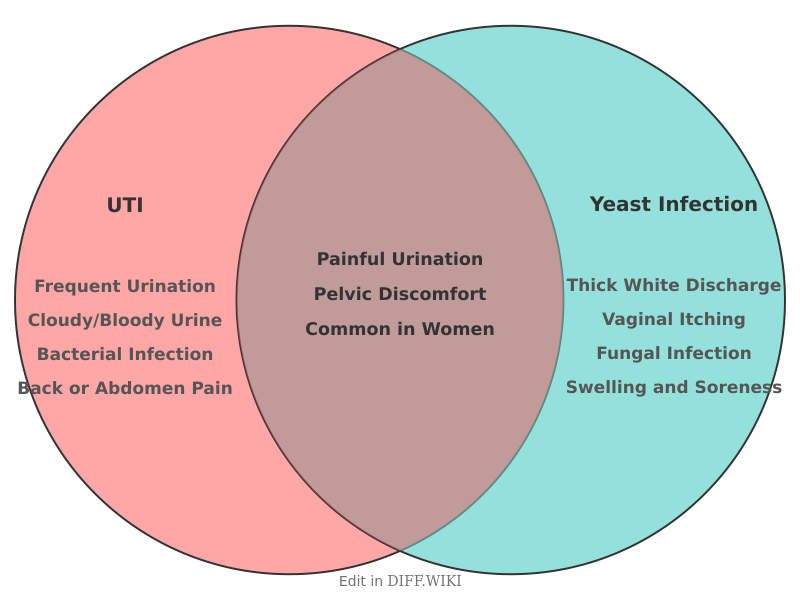
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a bacterial infection affecting any part of the urinary system, while a yeast infection is a fungal infection.[1] UTIs are most often caused by bacteria, whereas yeast infections result from an overgrowth of a fungus called *Candida*.[2] Both conditions are common, particularly in women, and can sometimes present with overlapping symptoms, though they require different treatments.[3][4]
UTIs primarily impact the urinary tract, which includes the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys.[5] Yeast infections typically affect the vagina and vulva in women.[5] While both can cause a burning sensation during urination, the nature of the symptoms often differs. UTIs are characterized by a persistent urge to urinate, frequent urination of small amounts, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. Yeast infections are more commonly associated with intense itching, irritation, and a thick, white, odorless vaginal discharge.[1]
It is possible to have both a UTI and a yeast infection simultaneously. Additionally, the antibiotic treatment for a UTI can sometimes disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora, leading to the development of a yeast infection.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | Yeast Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Causative Agent | Typically bacteria, such as *E. coli*.[5] | Fungus, most commonly *Candida* species.[2] |
| Affected Area | Urinary tract (bladder, urethra, kidneys).[5] | Vagina and vulva.[5][1] |
| Primary Symptoms | Frequent urge to urinate, painful urination, cloudy or bloody urine, pelvic pain.[5] | Vaginal itching, soreness, redness, swelling, and a thick, white discharge.[5] |
| Discharge | Does not typically cause vaginal discharge; urine may be cloudy or pinkish.[4] | Thick, white, clumpy, odorless vaginal discharge is common.[1] |
| Pain | Internal burning or stinging sensation during urination.[1] | Primarily external itching and irritation; a burning sensation may occur on the vulva from urine contact.[1] |
| Diagnosis | Urinalysis and urine culture to detect bacteria.[3] | Pelvic exam and microscopic examination or culture of a vaginal swab. |
| Treatment | Prescription antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria.[5] | Antifungal medications, available as oral pills, topical creams, or suppositories.[5] |
Prevention[edit]
Some preventative measures can help reduce the risk of developing both UTIs and yeast infections. General hygiene practices are beneficial for both. This includes wiping from front to back after using the toilet to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Specific strategies for preventing UTIs include staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water, which helps to flush bacteria from the urinary system. Urinating frequently and not holding in urine can also reduce risk.[4]
To help prevent yeast infections, it is advisable to wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid wearing tight-fitting pants or staying in wet clothing for extended periods. Avoiding the use of scented feminine products, such as sprays and harsh soaps, can also help maintain a healthy balance of vaginal flora.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "twentyeighthealth.com". Retrieved February 07, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "hellowisp.com". Retrieved February 07, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "healthline.com". Retrieved February 07, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "kaiserpermanente.org". Retrieved February 07, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 "redboxrx.com". Retrieved February 07, 2026.