Differences between GIF and PNG
GIF vs. PNG[edit]
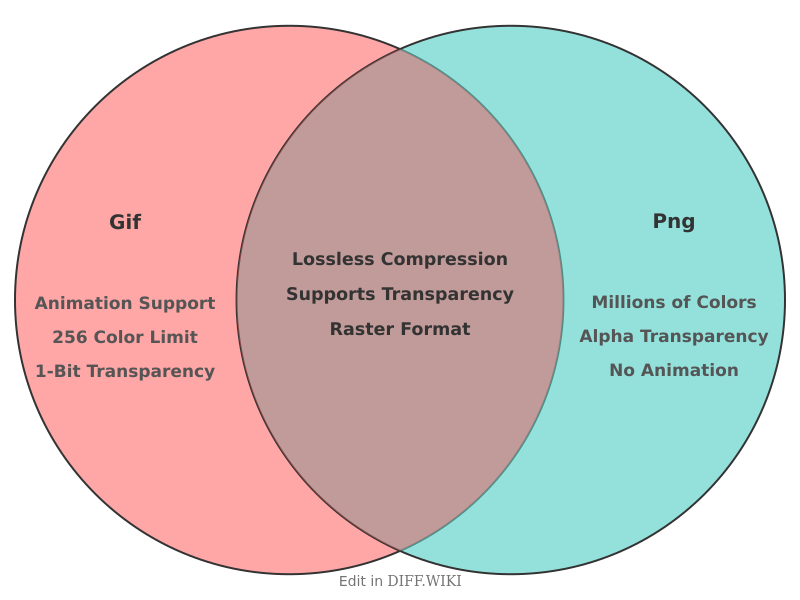
The Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) and Portable Network Graphics (PNG) are both raster graphics file formats that use lossless data compression.[1][2] PNG was developed as a successor to GIF, partly motivated by Unisys's enforcement of its patent on the LZW compression algorithm used by GIF.[1] While both formats are suitable for storing images with sharp lines and solid colors, they have distinct features that make them appropriate for different applications.[3][4]
One of the primary differences is their support for color depth.[5] GIF files use an 8-bit palette, which limits them to a maximum of 256 colors per frame.[3] In contrast, PNG files can support a much wider range of colors, including 24-bit truecolor (millions of colors), making them a better choice for images with complex colors and gradients.[3]
Transparency is another area where the two formats differ significantly. GIF supports only binary transparency, meaning a pixel can be either fully transparent or fully opaque. This can result in aliasing or jagged edges when an image is placed on a non-solid background.[5] PNG, on the other hand, supports an 8-bit alpha channel, allowing for 256 levels of partial transparency. This enables smooth blending of images with any background.[3]
Animation is a key feature of the GIF format, which allows for sequences of frames to create short, looping animations. Standard PNG files do not support animation. However, an extension to the format called Animated Portable Network Graphics (APNG) was developed to provide animation capabilities similar to GIF but with the superior color and transparency support of PNG.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | GIF | PNG |
|---|---|---|
| Color Depth | 8-bit (256 colors) | Up to 48-bit truecolor and 16-bit grayscale |
| Compression | LZW (Lossless) | DEFLATE (Lossless)[1] |
| Transparency | 1-bit (binary) | 8-bit alpha channel (partial transparency) |
| Animation | Supported | Not supported in standard PNG, but available in APNG extension |
| File Size | Generally smaller for simple animations and images with few colors[3][2] | Can be larger than GIF for simple images, but often smaller for complex images due to more efficient compression[5][3] |
| Best Use Cases | Simple animations, logos, and graphics with limited colors[4] | Logos, graphics needing transparency, and images with a wide range of colors[3][4] |
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "geeksforgeeks.org". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "cloudinary.com". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "medium.com". Retrieved January 08, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "piccolo2d.org". Retrieved January 08, 2026.