Differences between England and Great Britain
Contents
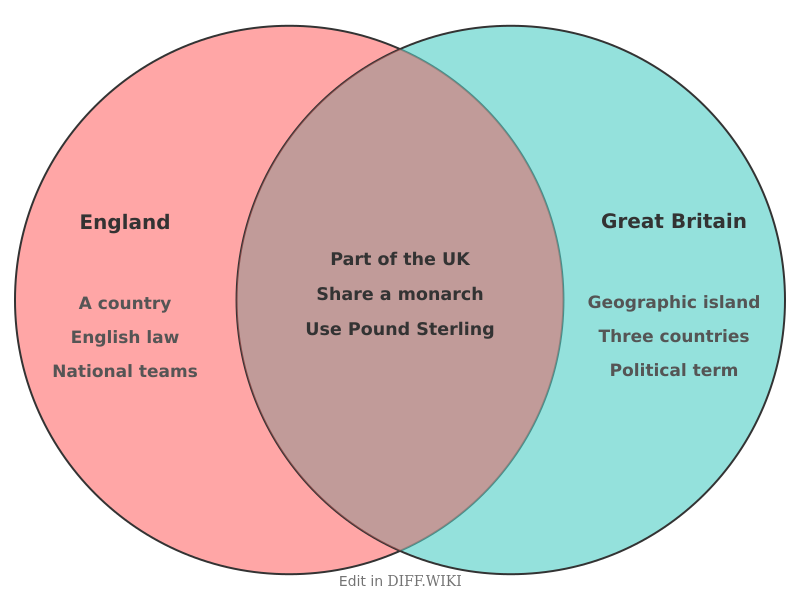
Distinction between England and Great Britain[edit]
The terms England, Great Britain, and the United Kingdom are often used interchangeably, but each has a distinct meaning.[1][2] England is a country, while Great Britain is the island that includes the countries of England, Wales, and Scotland.[3][4] The United Kingdom is a sovereign state that includes Great Britain and Northern Ireland.[5] Understanding these differences is based on their separate geographical and political contexts.[1][2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | England | Great Britain |
|---|---|---|
| Geographical Definition | A country on the island of Great Britain, sharing land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west.[4] | An island in the North Atlantic Ocean, situated off the north-west coast of mainland Europe.[3] |
| Entity Type | A constituent country of the United Kingdom.[4] | A geographical landmass and a political term referring to the union of England, Scotland, and Wales.[3][1] |
| Constituent Areas | The territory of England, including offshore islands such as the Isle of Wight. | The countries of England, Scotland, and Wales, and their respective islands, such as the Hebrides and Shetland.[3] |
| Political Status | A country within the sovereign state of the United Kingdom. It does not have its own separate government and is governed directly by the UK Parliament.[4] | The political entity of the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed by the Acts of Union in 1707, uniting the kingdoms of England and Scotland.[1] This union is now part of the United Kingdom. |
| Legal System | Operates under English law, which is also the legal system for Wales. | Contains two distinct legal systems: English law (for England and Wales) and Scots law (for Scotland). |
Political and historical context[edit]
The term Great Britain has both a geographical and a political dimension. Geographically, it is the largest island of the British Isles.[3] The name "Britain" derives from the Latin term Britannia, used by the Romans.[3] The "Great" was added in the Middle Ages to distinguish the island from the smaller region of Brittany in France, which was also settled by Britons.
Politically, the Kingdom of Great Britain was established in 1707 through the Acts of Union, which united the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland into a single state with one parliament. This union created a new political entity that covered the entire island.
England is one of the four constituent countries of the United Kingdom. Historically, it was an independent sovereign state, the Kingdom of England, which ceased to exist following the 1707 union with Scotland. Unlike Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland, England does not have a devolved parliament or assembly of its own and is governed on most matters by the UK Parliament, located in London. England, combined with Wales, forms a single legal jurisdiction within the United Kingdom's three distinct legal systems.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "britannica.com". Retrieved January 18, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "byjus.com". Retrieved January 18, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 18, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "britannica.com". Retrieved January 18, 2026.
- ↑ "worldatlas.com". Retrieved January 18, 2026.