Differences between Alprazolam and Clonazepam
Contents
Alprazolam vs. Clonazepam[edit]
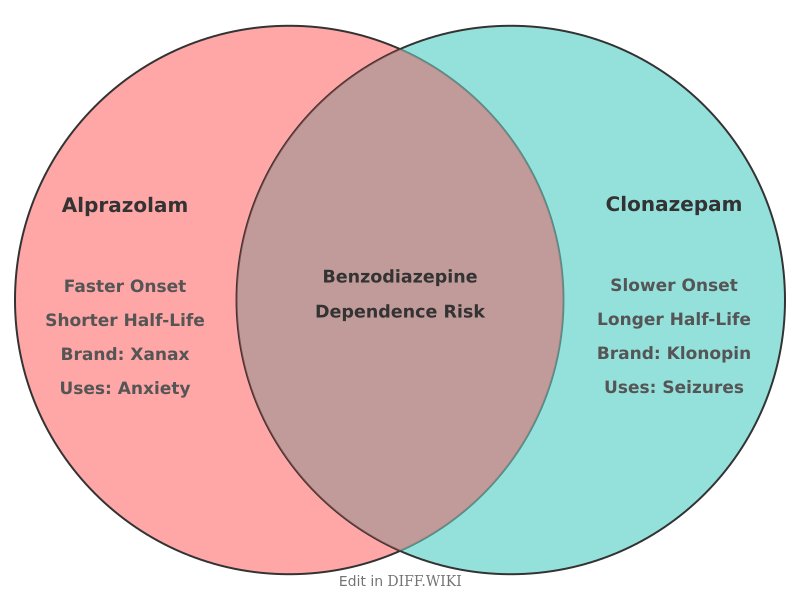
Alprazolam and clonazepam are both medications belonging to the benzodiazepine class, which act as central nervous system depressants.[1] They work by increasing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that produces a calming effect in the brain.[2][3] Both drugs are prescribed for the treatment of anxiety and panic disorders.[4][5] However, they have distinct differences in their approved uses, duration of action, and how quickly they take effect.
One of the primary distinctions lies in their approved medical uses. Alprazolam is FDA-approved for the management of anxiety disorders and panic disorder.[4] Clonazepam is also approved for panic disorder but is additionally used to treat certain seizure disorders in both adults and children.[1]
The pharmacokinetic profiles of the two drugs also differ significantly. Alprazolam is considered an intermediate-acting benzodiazepine.[2] It takes effect relatively quickly, with its effects felt within minutes and reaching peak concentrations in the blood within 1 to 2 hours. In contrast, clonazepam is a long-acting benzodiazepine.[2] It has a slower onset of action, taking 1 to 4 hours to reach its full effect, but its calming effects last longer, up to 12 hours or more. This is due to its longer half-life, which is the time it takes for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. Alprazolam has a half-life of about 6 to 25 hours, while clonazepam's half-life is significantly longer at 22 to 54 hours.
Due to its shorter half-life and rapid onset of action, alprazolam may be more suitable for the short-term relief of acute anxiety or panic attacks. The longer duration of action of clonazepam may make it a better option for the long-term management of chronic anxiety or seizure disorders, as it allows for less frequent dosing.[4] Both medications carry a risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Alprazolam | Clonazepam |
|---|---|---|
| Drug Class | Benzodiazepine | Benzodiazepine |
| Brand Names | Xanax, Xanax XR, Niravam | Klonopin, Rivotril[1] |
| Approved Uses | Anxiety disorders, Panic disorder[4] | Panic disorder, Seizure disorders |
| Onset of Action | Faster-acting (minutes to an hour) | Slower-acting (1-4 hours) |
| Half-Life | 6-25 hours | 22-54 hours |
| Duration of Action | Shorter-acting[2] | Longer-acting[2] |
| Common Side Effects | Drowsiness, dizziness, memory problems, slurred speech | Drowsiness, fatigue, motor impairment, dizziness |
| Potential for Dependence | High | High |
Pharmacology[edit]
Both alprazolam and clonazepam enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA at the GABA-A receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties.[2] This action is achieved by increasing the frequency of chloride channel opening, which leads to hyperpolarization of the neuron and reduced neuronal excitability.[3]
Alprazolam is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme. Clonazepam is also metabolized by the liver, primarily through nitroreduction by cytochrome P450 enzymes, including CYP3A4. The difference in their chemical structure contributes to their varying rates of metabolism and, consequently, their different half-lives and durations of action.
Clinical Considerations[edit]
The choice between alprazolam and clonazepam depends on the specific condition being treated, the desired onset and duration of effect, and individual patient factors. For instance, the faster onset of alprazolam may be preferable for treating sudden panic attacks. Conversely, the longer duration of clonazepam can provide more consistent control of symptoms in chronic anxiety or seizure disorders, with the convenience of less frequent dosing.[4]
Both medications can cause significant side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and impaired coordination. Long-term use of either drug can lead to tolerance, physical dependence, and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.[2] Due to its shorter half-life, alprazolam may have a higher potential for causing rebound anxiety and more severe withdrawal symptoms between doses. It is important for these medications to be used under the close supervision of a healthcare provider.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "healthline.com". Retrieved February 06, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "study.com". Retrieved February 06, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "goodrx.com". Retrieved February 06, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "buzzrx.com". Retrieved February 06, 2026.
- ↑ "delphihealthgroup.com". Retrieved February 06, 2026.